Managing Inventory Items
Learn how to create, edit, and manage inventory items to track your stock levels effectively.
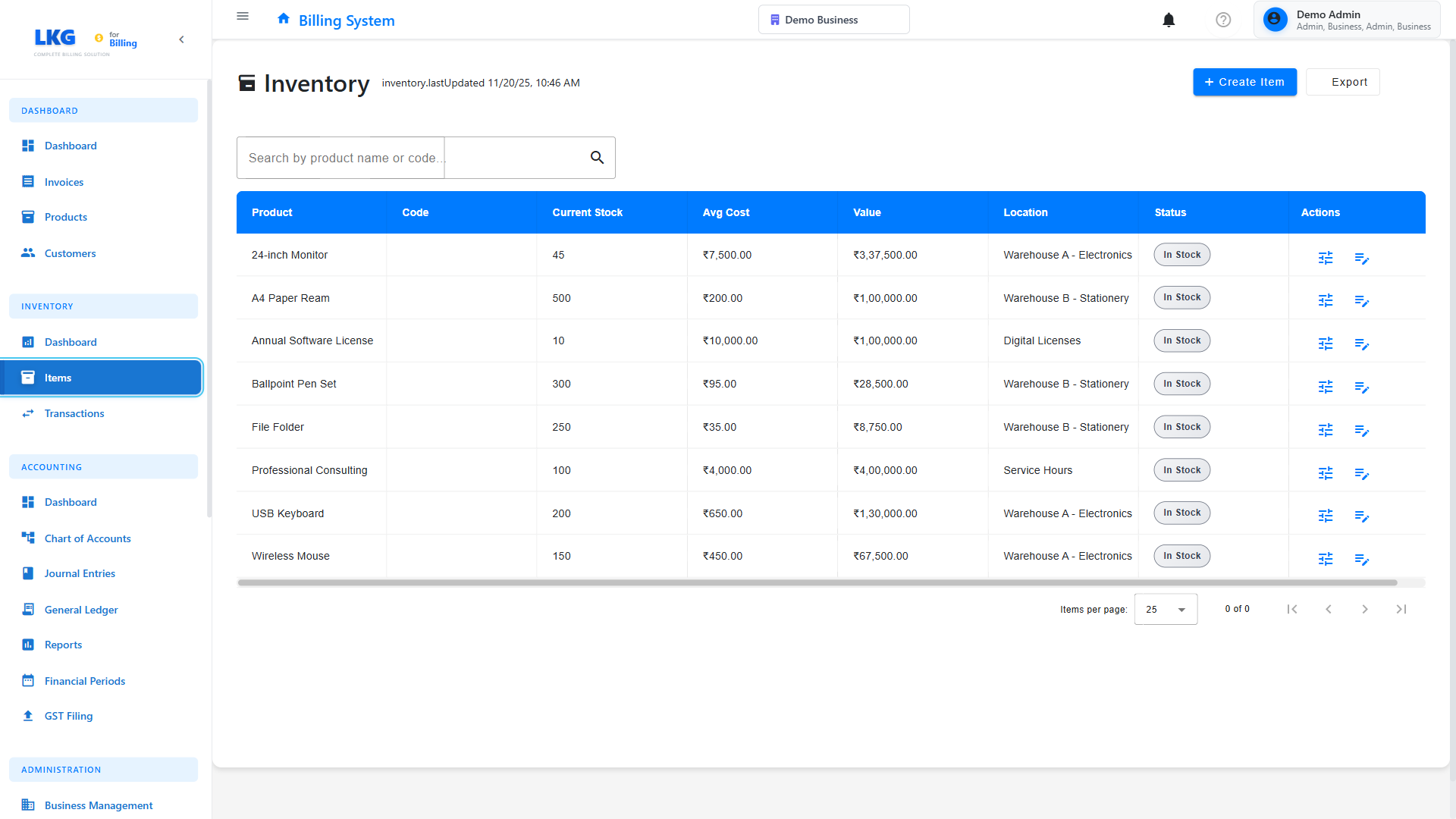
Inventory Items List
The Inventory Items page displays all products you're tracking with their current stock status.
Viewing Inventory
The inventory list shows:
- Product Name - Name and SKU of the item
- Current Stock - Available quantity
- Minimum Stock - Reorder threshold
- Unit Cost - Cost per unit
- Total Value - Current stock × unit cost
- Status - Stock level indicator
- 🟢 In Stock - Above minimum level
- 🟡 Low Stock - At or near minimum level
- 🔴 Out of Stock - Zero quantity
Quick Actions
From the inventory list, you can:
- View Details - See complete item information
- Adjust Stock - Add or remove stock
- Edit Item - Update product details
- View History - See all transactions
Creating an Inventory Item
Step 1: Start New Item
- Navigate to Inventory → Items
- Click "Create Item" button
- The inventory item form opens
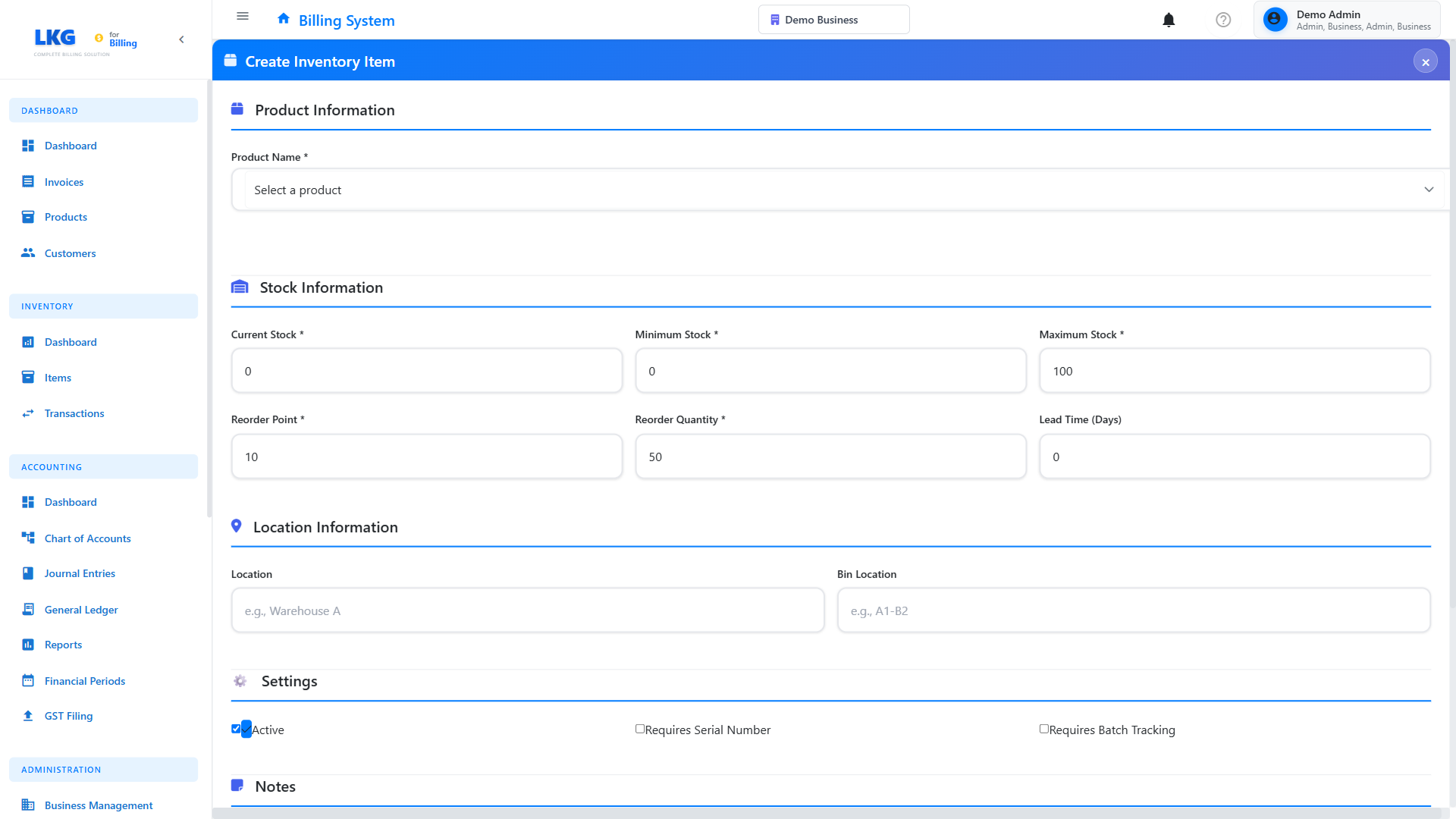
Step 2: Enter Basic Information
Product Selection (Required)
Select the product from your product catalog. Only products that don't already have inventory items can be selected.
SKU/Product Code
- Automatically filled from product
- Can be edited if needed
- Must be unique across inventory
Current Stock Quantity (Required)
The initial quantity you have in stock:
Examples:
- 100 (100 units)
- 50.5 (50.5 kg for weight-based items)
- 0 (if setting up before receiving stock)
Minimum Stock Level (Required)
The threshold that triggers low stock alerts:
Examples:
- 10 (reorder when 10 or fewer remain)
- 25 (for high-demand items)
- 5 (for slow-moving items)
Maximum Stock Level
Optional upper limit for reordering:
Example:
- Minimum: 10
- Maximum: 100
- Reorder when: ≤ 10
- Order quantity: to reach 100
Step 3: Cost Information
Unit Cost (Required)
The cost per unit of the product:
Examples:
- ₹500 (cost price per unit)
- ₹1,250 (average cost for varying prices)
Unit cost is used to calculate inventory value. Update it when you purchase at different prices to maintain accurate valuation.
Unit of Measure
Specify how the product is measured:
- Piece/Unit - Individual items
- Box/Carton - Packaged quantities
- Kg/Gram - Weight-based
- Liter/ML - Volume-based
- Meter - Length-based
Step 4: Storage & Location
Storage Location
Physical location where item is stored:
Examples:
- "Warehouse A - Shelf 12"
- "Main Store - Section B3"
- "Cold Storage - Bay 5"
Bin/Rack Number
Specific storage identifier:
Examples:
- "A-12-03"
- "R15-S02"
- "CS-05-L"
Step 5: Save the Item
- Review all entered information
- Click "Save" button
- The new inventory item appears in the list
- Initial stock quantity is recorded as a transaction
Editing Inventory Items
Update Item Details
-
Find the item in the inventory list
-
Click the Edit icon
-
Modify the fields:
- Unit cost (affects future calculations)
- Minimum/maximum stock levels
- Storage location
- Product details
-
Click "Save" to apply changes
Don't change current stock quantity through edit. Use Stock Adjustments to change quantities - this maintains proper transaction history.
Stock Level Indicators
Status Colors
🟢 In Stock (Green)
Current Stock > Minimum Stock
Example: Current: 50, Minimum: 10
Status: Healthy stock level
🟡 Low Stock (Yellow)
Minimum Stock < Current Stock ≤ (Minimum Stock × 1.5)
Example: Current: 12, Minimum: 10
Status: Order soon
🔴 Out of Stock (Red)
Current Stock = 0
Status: Urgent - Cannot fulfill orders
Inventory Valuation
Total inventory value is calculated as:
Total Value = Current Stock × Unit Cost
Example:
- Product A: 50 units × ₹500 = ₹25,000
- Product B: 30 units × ₹1,200 = ₹36,000
- Product C: 75 units × ₹300 = ₹22,500
----------------------------------------
Total Inventory Value = ₹83,500
Bulk Operations
Export Inventory Data
Export your inventory for:
- Backup purposes
- External analysis
- Reporting to stakeholders
- Audit requirements
- Click "Export" button
- Choose format (CSV, Excel)
- Download the file
Import Inventory (Future Feature)
Bulk import capabilities coming soon for:
- Initial setup with large catalogs
- Regular stock updates
- Migration from other systems
Best Practices
Setting Minimum Stock Levels
Calculate based on:
-
Average Daily Sales
If you sell 5 units/day on average:
Minimum Stock = 5 × Lead Time Days + Safety Buffer
Example: 5 × 7 days + 5 buffer = 40 units -
Lead Time
- Time to reorder and receive stock
- Add buffer for delays
-
Sales Variability
- Higher variability = higher minimum
- Seasonal peaks require adjustment
Maintaining Accurate Costs
Update unit costs when:
- ✅ Purchasing at new price
- ✅ Receiving supplier price updates
- ✅ Costs include shipping/duties
- ✅ Volume discounts affect average cost
Cost calculation methods:
- FIFO (First In, First Out) - Use oldest cost
- Average Cost - Calculate weighted average
- Last Purchase - Use most recent cost
Storage Organization
Organize by:
- Product category
- Sales frequency (fast-movers near front)
- Size/weight
- Special requirements (temperature, security)
Troubleshooting
Cannot Create Inventory Item
Problem: Product not available in dropdown
Solutions:
- Check if product already has an inventory item
- Create the product first in Products module
- Ensure product is active
Incorrect Stock Value
Problem: Total value seems wrong
Solutions:
- Verify unit cost is correct
- Check current stock quantity
- Review recent transactions
- Make stock adjustment if needed
Missing Items in List
Problem: Cannot find an inventory item
Solutions:
- Use search feature
- Check if item was deleted
- Verify filters are not applied
- Refresh the page
Next Steps
- Stock Adjustments - Learn how to adjust stock levels
- Transaction History - View all stock movements
- Inventory Dashboard - Monitor overall inventory health
Pro Tip: Review and update your minimum stock levels quarterly based on actual sales patterns to optimize inventory management.